Objective
To determine the stress–strain state of a beam with a tie, taking into account transverse shear deformations in the beam.
Reference
M. Laredo, Résistance des matériaux, Paris, Dunod, 1970, P. 77.
Problem statement
Determine:
-
the axial force in the tie PE,
-
the bending moment M in the beam at point H,
-
the vertical displacement v (Z) at point D.
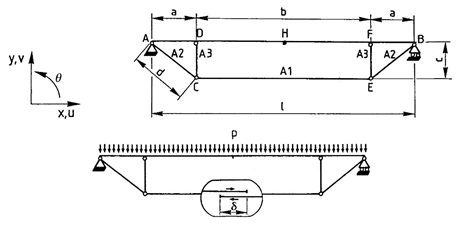
Design model
A single-span beam is provided with a tie which is tensioned by an imposed displacement δ and is loaded by a uniformly distributed load q.
Geometry
Length of bars: à = 2 m; b = 4 m; l = 8 m; ñ = 0,6 m; d = 2,088 m.
Cross-sectional area of beam AD, DF, FB : À = 0,01516 m2; Àr = A/2,5 = 0,006064 m2;
Moment of inertia of beam: I = 2,174 * 10-4 m4;
Cross-sectional area of bars AC, CE, EB: À1 = À2 = 4.5 * 10-3 m2;
Cross-sectional area of bars DC, FE: À3 = 3,48 * 10-3 m2.
Material properties
Modulus of elasticity Å = 2,1 * 1011 Pa.
Shear modulus G = 0,4 * Å = 0,84 * 1011 Pa.
Boundary conditions
At points A and B, restraints preventing vertical displacement along the global Z-axis are applied
Z (v_A, v_B) = 0.
At point H, a restraint preventing horizontal displacement along the global X-axis is applied
(X (u_H) = 0) to ensure symmetry of displacements.
Loads
Uniformly distributed load q = 50000 N/m.
Displacement δ = 6,52 * 10-3 m.
Note
The problem is solved in a plane formulation (model type 2 – XOZ plane).
FE types used:
-
FE type 1 – FE of 2D truss is used to model the tie elements (AC, CE, EB) and the struts (DC, FE). Nodes of FE 1 have two degrees of freedom (translations along the global X and Z axes), therefore the connections of these elements at the nodes are pinned.
-
FE type 2 – FE of 2D frame (including shear) is used to model the beam elements (AD, DF, FB).
To apply the forced displacement of the tie, the FE representing the tie was split into two elements with duplicated nodes (option "to throw apart nodes"). The load was applied to each of the duplicated nodes.
In this case, the forced displacement of each node is δi = δ/2 = 3,26 * 10-3 m.
Number of nodes: 9. Number of elements: 12.
Output data
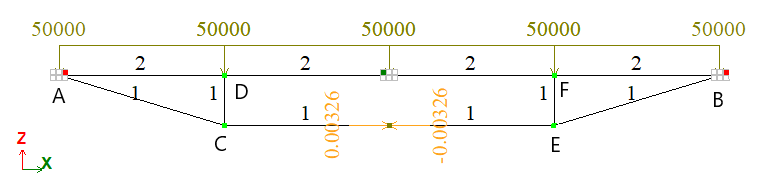
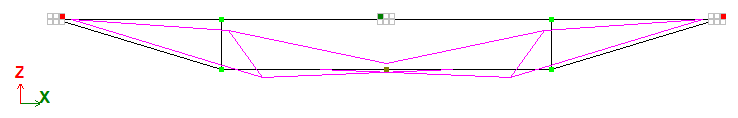
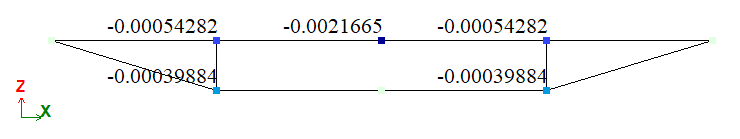
|
Design and deformed models of a beam |
Mosaic plot of vertical displacements v(Z), m |
|
Mosaic plot of axial forces N |
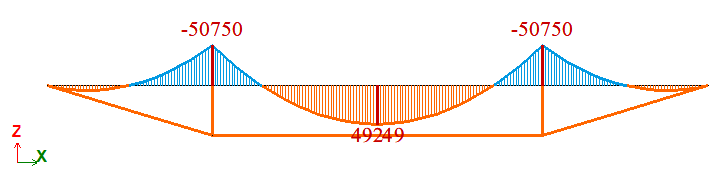
Diagram of bending moments M, N*m |
Analytical solution
μ = 1-(4/3)(a/l)
k = A/Ar = 2,5
t = √(I/A)
γ = (l/c)2(1+(A/A1)(b/l)+2(A/A2)(d/a)2(d/l)+2(A/A3)(C/A)2(c/a)2(c/l))
τ = k(2Et2/(Gal))
ρ = μ+γ+τ
μ0 = 1-(a/l)2(2-a/l)
τ0 = 6k(E/G)(t/l)2(1+b/l)
ρ0 = μ0+ τ0
NCE = -(1/12)(pl2/c)(ρ0/ρ)+(EI/(lc2))(δ/ρ)
MH = -(1/8)pl2(1-(2/3)(ρ0/ρ))-(EI/(lc))(δ/ρ)
Comparison of calculation results
| Point | The unknown | Analytical solution | LIRA-FEM | Error, % |
| ÑÅ | Axial force, N | 584584 | 58458 | 0,0007 |
| Í | Moment M, N*m | 49249,5 | 49249,5 | 0 |
| D | Displacement vD, m | -0,0005428 | -0,0005428 | 0 |
Download verification test
If you find a mistake and want to inform us about it, select the mistake, then hold down the CTRL key and click ENTER.

Comments