Objective
To determine the stress–strain state of a plane truss under the concentrated load.
Reference
S. Timoshenko, Resistance des materiaux, t.1, Bruxelles, Edition Polytechnique Beranger, 1963, p. 10.
Problem statement
To determine the vertical displacement Z of the common joint of the truss members and the axial forces N in the truss members.
Design model
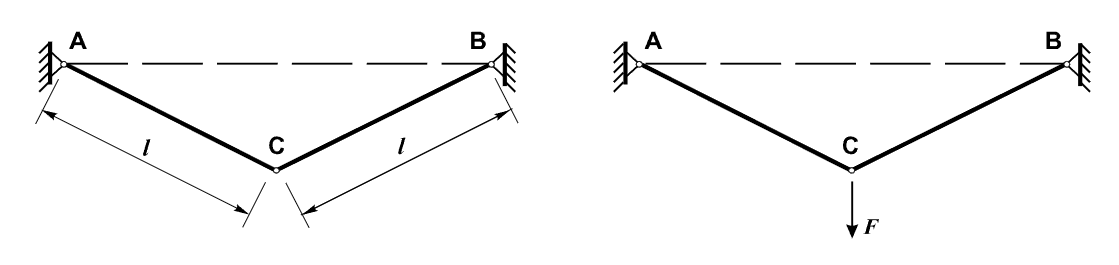
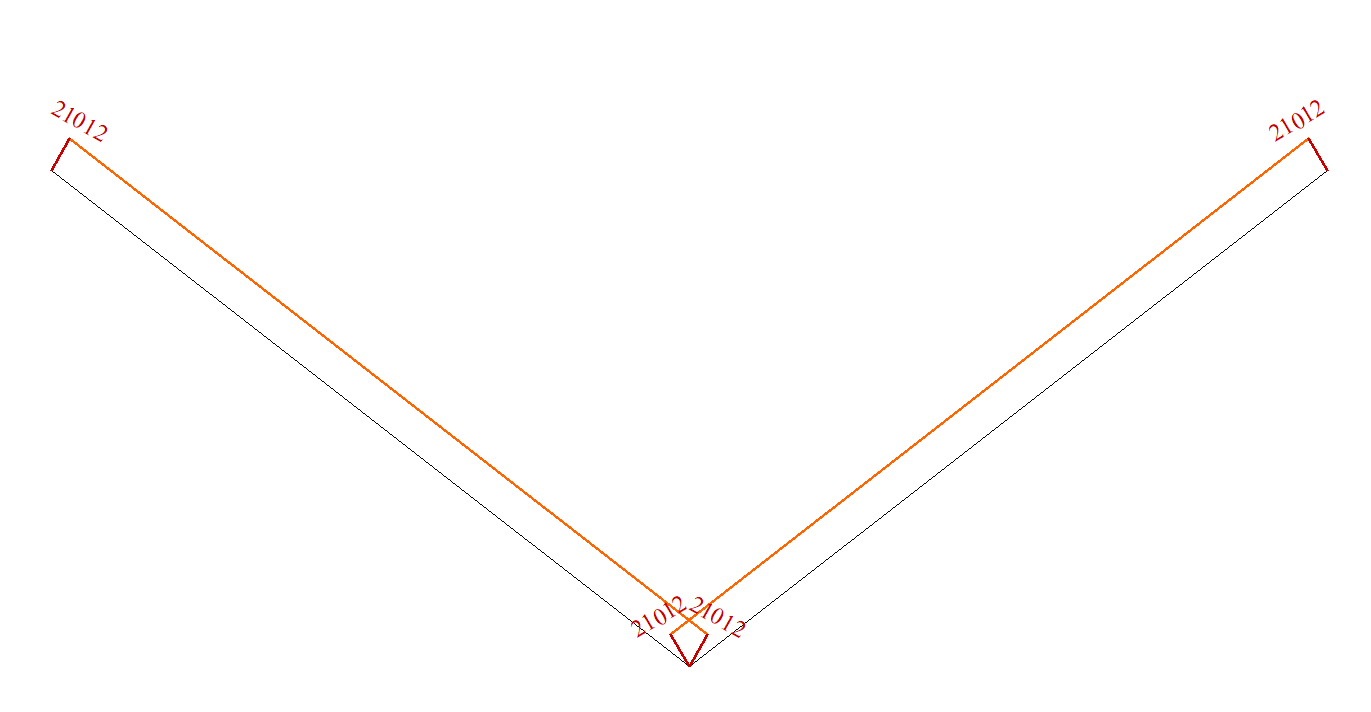
The plane truss consists of two inclined downward members of equal length and identical cross-sectional stiffness, arranged symmetrically about the vertical axis. The members are pin-connected at a common joint (point C) and are supported by pin supports at the opposite joints (points A and B). A vertical concentrated load F is applied at the common joint of the truss members.
Geometry
Element length L = 4.5 m;
Inclination angle of the elements to the horizontal θ = 30º
Cross-sectional area A = 3 * 10-4 m2;
Material properties
Modulus of elasticity Å = 2.1 * 1011 Pa.
Loads
Vertical concentrated load: F = 21 kN.
Note
The design model is a plane pin-jointed bar system consisting of two bar elements of type 1.
The boundary conditions are specified by imposing restraints in the X and Z directions at the pinned support nodes.
Number of nodes in design model: 3.
Output data
Comparison of calculation results
| Parameter | Analytical solution | LIRA-FEM | Error, % |
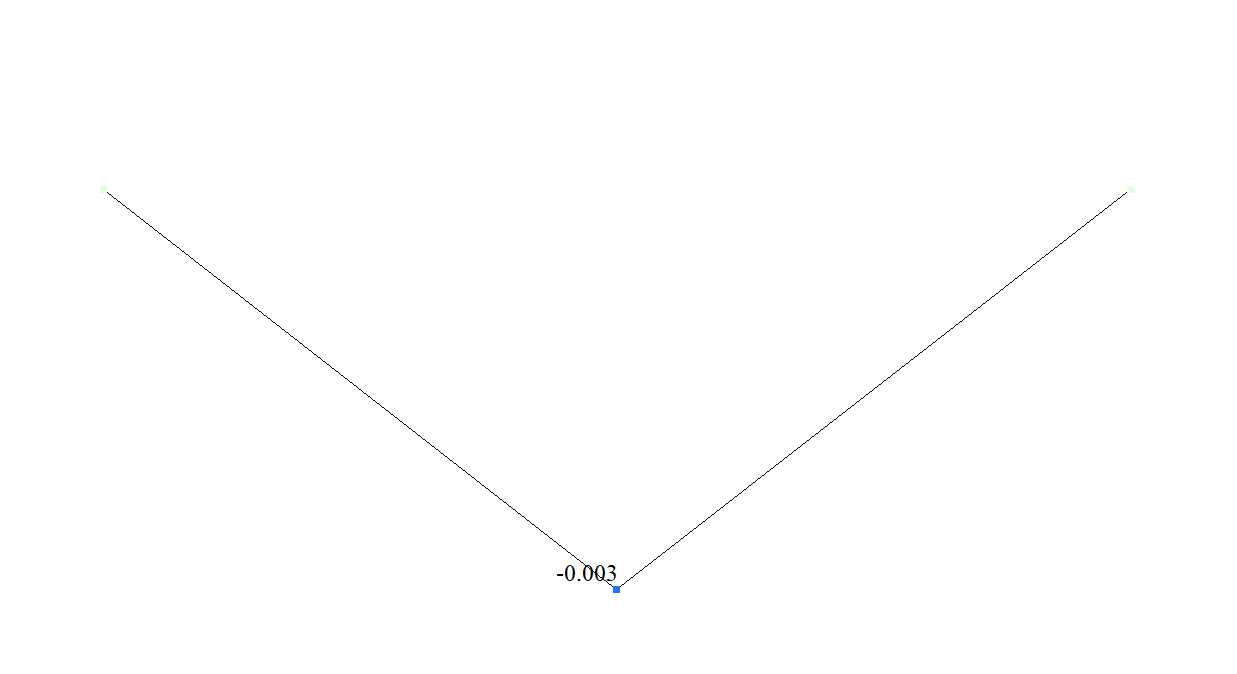
| Vertical displacement Z (point Ñ), m | -0,003 | -0,003 | 0 |
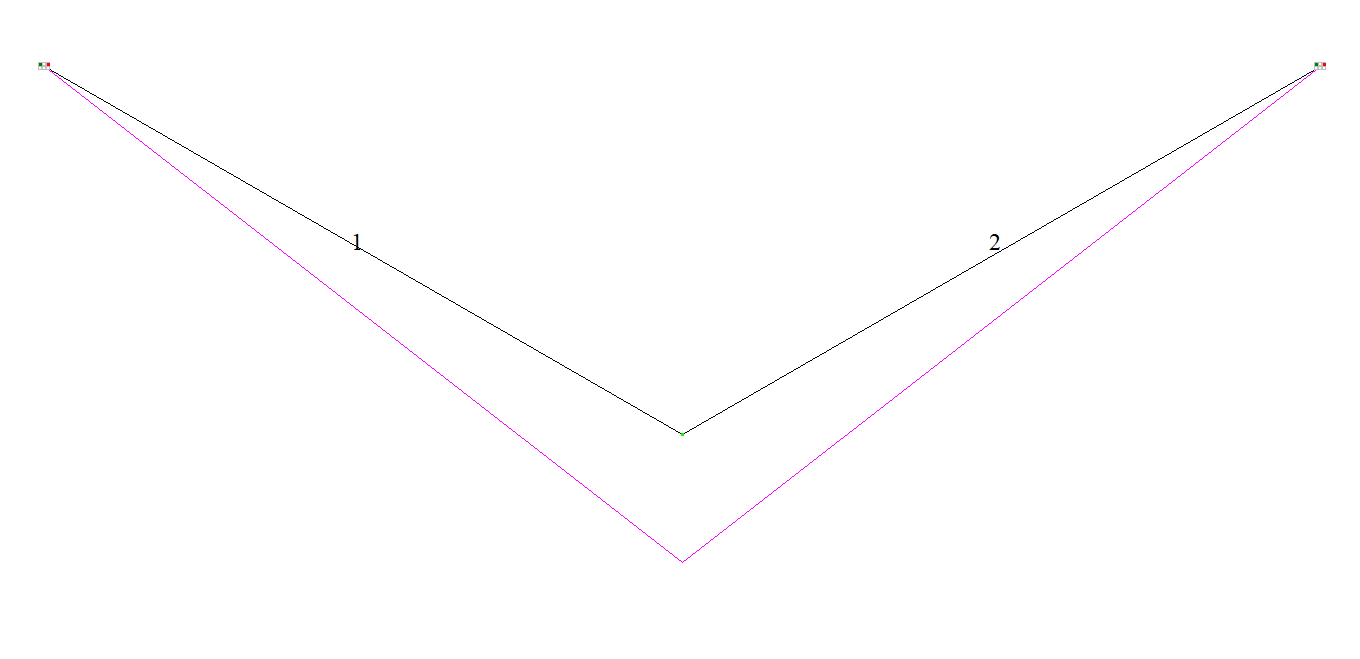
| Axial force N (element AC), N | 21000,0 | 21012,0 | 0,05 |
| Axial force N (element BC), N | 21000,0 | 21012,0 | 0,05 |
Download verification test
If you find a mistake and want to inform us about it, select the mistake, then hold down the CTRL key and click ENTER.
Comments