Objective
To determine the stress–strain state of a beam fixed at both ends under the uniformly distributed load, concentrated axial and transverse forces, and a bending moment.
Reference
S. Timoshenko, Resistance des materiaux, t.1, Paris, Eyrolles, 1976, p. 26. M. Courtand et P. Lebelle, Formulaire du beton arme, t.2, Paris, Eyrolles, 1976, p. 219.
Problem statement
To determine the vertical displacement Z, the axial force N, and the bending moment M at mid-span of the beam (point G), as well as the horizontal reaction H at the left end (point A).
Design model
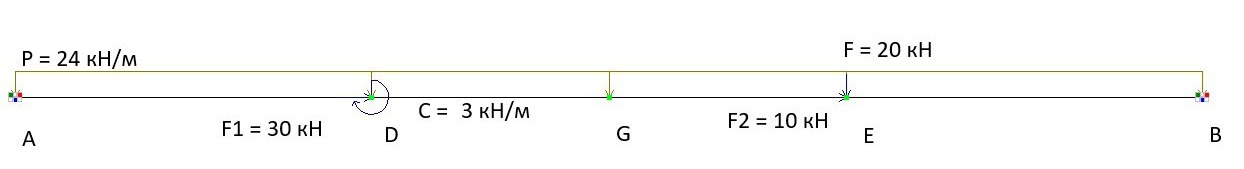
A beam fixed at both ends is subjected to:
– a uniformly distributed load P acting over the entire span length l;
– co-directional concentrated axial forces F1 and F2, located at a distance of 0.3l from the left and right ends, respectively;
– a concentrated transverse force F, located at a distance of 0.3l from the right end;
– a concentrated bending moment C, located at a distance of 0.3l from the left end.
Geometry
Beam length L = 1 m
Moment of inertia J = 1,7 * 10-8 m4
Material properties
Modulus of elasticity Å = 2,0 * 1011 Pa
Poisson's ratio ν = 0,2
Loads
Uniformly distributed load Ð = 24 kN/m;
Concentrated force F1 = 30 kN;
Concentrated force F2 = 10 kN;
Concentrated force F = 20 kN;
Concentrated bending moment C = 3 kN.
Note
The design model is a general-purpose system consisting of 4 bar elements of type 10.
The boundary conditions at the fixed ends are defined by restraints applied in the directions of the following degrees of freedom:
– X, Y, Z — translational degrees of freedom;
– UX, UY, UZ — rotational degrees of freedom.
Number of nodes in the design model: 5.
Output data
Comparison of calculation results
| Parameter | Analytical solution | LIRA-FEM | Error, % |
| Vertical displacement Z (point G) (m) | -4,9023·10-2 | -4,9023·10-2 | 0 |
| Axial force N (point G) (N): | -6000,0 | -6000,0 | 0 |
| Bending moment M (point G) (kN*m) | -2800,0 | -2800,0 | 0 |
| Horizontal reaction H (point A) (N) | 24000,0 | 24000,0 | 0 |
Download verification test
If you find a mistake and want to inform us about it, select the mistake, then hold down the CTRL key and click ENTER.




Comments