Objective
To determine the stress–strain state of a beam on an elastic foundation under the concentrated forces and a distributed load varying according to a triangular law.
Problem statement
To determine the vertical displacements Z at the beam ends, as well as the bending moments My, shear forces Qz, and rotation angles uY along the beam length.
Design model
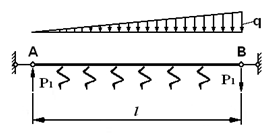
A beam on an elastic foundation subjected to mutually balanced concentrated forces applied at the ends and to a distributed load varying along the beam length according to a triangular law.
Geometry
Length l = 10 m
Moment of inertia I = 2 * 10-6 m4
Cross-sectional area A = 0,003 m2
Shear area F = 0,0025 m2
Material properties
Modulus of elasticity Å = 2,1 * 107 tf/m2
Shear modulus G = 7,875 * 106 tf/m2
Boundary conditions
Parameters of elastic foundation: Ñ1 = 500 tf/m3; Ñ2 = 100 tf/m. Restraints are applied at the beam ends in the degrees of freedom (DOF) that prevent displacement along the X-axis of the beam (uA = u = 0).
Loads
Nonuniformly distributed load: q = 50 tf/m.
Vertical concentrated force: Ð1 = −Ð1 = 1 tf.
Note
The problem is solved in a plane formulation (model type 2 – displacements X, Z, Uy).
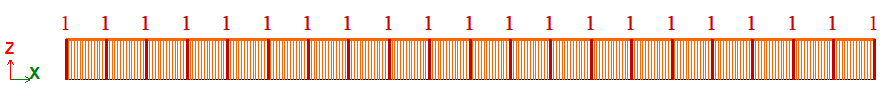
The model is generated with FE type 10 – arbitrary 3D bar.
The elastic foundation is described by two subgrade moduli (Pasternak model), specified for a settlement trough width of Âñ = 100 cm.
Number of nodes: 21. Number of elements: 20.
Output data
Analytical solution
w = −qx / (C1q)
M = 0
Q = −C2q / C1
Comparison of calculation results
| Point | The unknown | Analytical solution | LIRA-FEM | Error, % |
| À | Displacement wA, m | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Â | Displacement wB, m | -0,1 | -0,1 | 0 |
| Any | Rotation angle θY, rad | 0,01 | 0,01 | 0 |
| Force Qz, tf | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| Moment Ìy, tf*m | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Download verification test
If you find a mistake and want to inform us about it, select the mistake, then hold down the CTRL key and click ENTER.
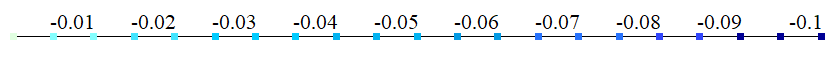
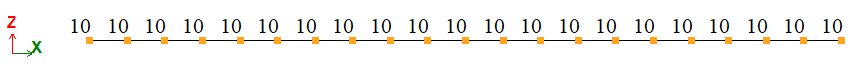
Comments